Python字典
Python 中的字典是键值的集合,用于像地图一样存储数据值,这与其他仅将单个值作为元素的数据类型不同。
Python 中的字典示例
字典包含键:值对。字典中提供了Key-Value,使其更加优化。
- Python3
Dict = {1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
print(Dict)
输出:
{1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
创建字典
在Python中,可以通过将一系列元素放置在大括号{}内并以“逗号”分隔来创建字典。Dictionary 包含成对的值,一个是 Key,另一个对应的成对元素是它的Key:value。字典中的值可以是任何数据类型并且可以重复,而键不能重复并且必须是不可变的。
注意 –字典键是区分大小写的,相同名称但不同大小写的键将被区别对待。
- Python3
# Creating a Dictionary
# with Integer Keys
Dict = {1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
print("\nDictionary with the use of Integer Keys: ")
print(Dict)
# Creating a Dictionary
# with Mixed keys
Dict = {'Name': 'Geeks', 1: [1, 2, 3, 4]}
print("\nDictionary with the use of Mixed Keys: ")
print(Dict)
输出:
使用整数键的字典:
{1: '极客', 2: '为了', 3: '极客'}
使用混合键的字典:
{'姓名': '极客', 1: [1, 2, 3, 4]}
字典也可以通过内置函数 dict() 创建。只需放置到花括号{} 即可创建一个空字典。
- Python3
# Creating an empty Dictionary
Dict = {}
print("Empty Dictionary: ")
print(Dict)
# Creating a Dictionary
# with dict() method
Dict = dict({1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'})
print("\nDictionary with the use of dict(): ")
print(Dict)
# Creating a Dictionary
# with each item as a Pair
Dict = dict([(1, 'Geeks'), (2, 'For')])
print("\nDictionary with each item as a pair: ")
print(Dict)
输出:
Empty Dictionary:
{}
Dictionary with the use of dict():
{1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
Dictionary with each item as a pair:
{1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For'}
创建字典的复杂性:
时间复杂度: O(len(dict))
空间复杂度: O(n)
嵌套字典
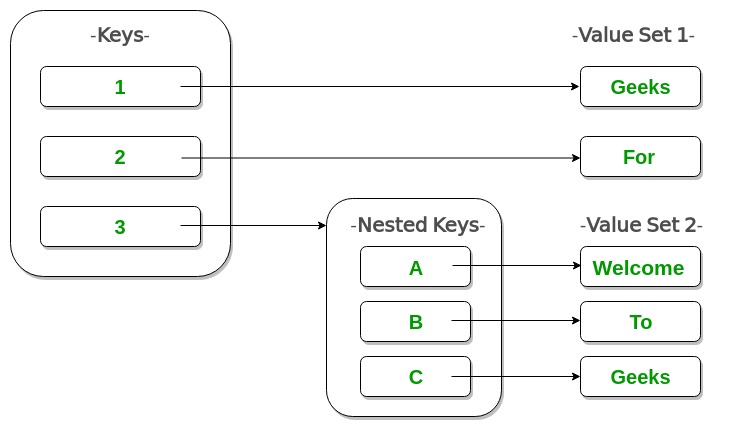
# Creating a Nested Dictionary
# as shown in the below image
Dict = {1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For',
3: {'A': 'Welcome', 'B': 'To', 'C': 'Geeks'}}
print(Dict)
输出:
{1: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: {'A': 'Welcome', 'B': 'To', 'C': 'Geeks'}}
向字典中添加元素
可以通过多种方式添加元素。通过定义值和键,例如 Dict[Key] = 'Value',一次可以将一个值添加到字典中。可以使用内置的update()方法更新字典中的现有值。嵌套键值也可以添加到现有词典中。
注意 -添加值时,如果键值已经存在,则该值将被更新,否则会将具有该值的新键添加到字典中。
- Python3
# Creating an empty Dictionary
Dict = {}
print("Empty Dictionary: ")
print(Dict)
# Adding elements one at a time
Dict[0] = 'Geeks'
Dict[2] = 'For'
Dict[3] = 1
print("\nDictionary after adding 3 elements: ")
print(Dict)
# Adding set of values
# to a single Key
Dict['Value_set'] = 2, 3, 4
print("\nDictionary after adding 3 elements: ")
print(Dict)
# Updating existing Key's Value
Dict[2] = 'Welcome'
print("\nUpdated key value: ")
print(Dict)
# Adding Nested Key value to Dictionary
Dict[5] = {'Nested': {'1': 'Life', '2': 'Geeks'}}
print("\nAdding a Nested Key: ")
print(Dict)
输出:
Empty Dictionary:
{}
Dictionary after adding 3 elements:
{0: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 1}
Dictionary after adding 3 elements:
{0: 'Geeks', 2: 'For', 3: 1, 'Value_set': (2, 3, 4)}
Updated key value:
{0: 'Geeks', 2: 'Welcome', 3: 1, 'Value_set': (2, 3, 4)}
Adding a Nested Key:
{0: 'Geeks', 2: 'Welcome', 3: 1, 'Value_set': (2, 3, 4), 5:
{'Nested': {'1': 'Life', '2': 'Geeks'}}}
在字典中添加元素的复杂性:
时间复杂度: O(1)/O(n)
空间复杂度: O(1)
访问字典的元素
为了访问字典的项目,请参考其键名。键可以在方括号内使用。
# Python program to demonstrate
# accessing a element from a Dictionary
# Creating a Dictionary
Dict = {1: 'Geeks', 'name': 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
# accessing a element using key
print("Accessing a element using key:")
print(Dict['name'])
# accessing a element using key
print("Accessing a element using key:")
print(Dict[1])
输出:
Accessing a element using key:
For
Accessing a element using key:
Geeks
还有一个名为get()的方法也有助于从字典中访问元素。此方法接受键作为参数并返回值。
访问字典中元素的复杂性:
时间复杂度: O(1)
空间复杂度: O(1)
# Creating a Dictionary
Dict = {1: 'Geeks', 'name': 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
# accessing a element using get()
# method
print("Accessing a element using get:")
print(Dict.get(3))
输出:
Accessing a element using get:
Geeks访问嵌套字典的元素
为了访问嵌套字典中任何键的值,请使用索引 [] 语法。
# Creating a Dictionary
Dict = {'Dict1': {1: 'Geeks'},
'Dict2': {'Name': 'For'}}
# Accessing element using key
print(Dict['Dict1'])
print(Dict['Dict1'][1])
print(Dict['Dict2']['Name'])
输出:
{1: 'Geeks'}
Geeks
For
使用 del 关键字删除元素
可以使用 del 关键字删除字典的项目,如下所示。
# Python program to demonstrate
# Deleting Elements using del Keyword
# Creating a Dictionary
Dict = {1: 'Geeks', 'name': 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
print("Dictionary =")
print(Dict)
#Deleting some of the Dictionar data
del(Dict[1])
print("Data after deletion Dictionary=")
print(Dict)
输出
Dictionary ={1: 'Geeks', 'name': 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
Data after deletion Dictionary={'name': 'For', 3: 'Geeks'}
字典方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| dic.clear() | 从字典中删除所有元素 |
| dict.copy() | 返回字典的副本 |
| dict.get(key, default = “None”) | 返回指定键的值 |
| 字典.items() | 返回一个列表,其中包含每个键值对的元组 |
| dict.items() | 返回包含字典键的列表 |
| popItem() | 用指定的键值对更新字典 |
| dict.values() | 返回字典所有值的列表 |
| pop() | 删除具有指定键的元素 |
| popItem() | 删除最后插入的键值对 |
| dict.setdefault(key,default= “None”) | 如果字典中没有指定键,则将键设置为默认值 |
| dict.has_key(key) | 如果字典包含指定的键,则返回 true。 |
| dict.get(key, default = “None”) | 用于获取为传递的键指定的值。 |
- Python3
# demo for all dictionary methods
dict1 = {1: "Python", 2: "Java", 3: "Ruby", 4: "Scala"}
# copy() method
dict2 = dict1.copy()
print(dict2)
# clear() method
dict1.clear()
print(dict1)
# get() method
print(dict2.get(1))
# items() method
print(dict2.items())
# keys() method
print(dict2.keys())
# pop() method
dict2.pop(4)
print(dict2)
# popitem() method
dict2.popitem()
print(dict2)
# update() method
dict2.update({3: "Scala"})
print(dict2)
# values() method
print(dict2.values())
输出:
{1: 'Python', 2: 'Java', 3: 'Ruby', 4: 'Scala'}
{}
Python
dict_items([(1, 'Python'), (2, 'Java'), (3, 'Ruby'), (4, 'Scala')])
dict_keys([1, 2, 3, 4])
{1: 'Python', 2: 'Java', 3: 'Ruby'}
{1: 'Python', 2: 'Java'}
{1: 'Python', 2: 'Java', 3: 'Scala'}
dict_values(['Python', 'Java', 'Scala'])
原文链接:codingdict.net
