Python If Else
Python 中的控制流类型
在Python编程语言中,控制流语句的类型如下:
- if 语句
- if-else 语句
- 嵌套 if 语句
- if-elif-else 阶梯
if 语句
if 语句是最简单的决策语句。它用于决定是否执行某个语句或语句块。
语法:
if condition:
# Statements to execute if
# condition is true此处,评估后的条件将为真或假。如果语句接受布尔值——如果值为真,那么它将执行下面的语句块,否则不执行。
众所周知,python 使用缩进来标识块。因此 if 语句下的块将被识别,如下例所示:
if condition:
statement1
statement2
# Here if the condition is true, if block
# will consider only statement1 to be inside
# its block.Python if语句流程图
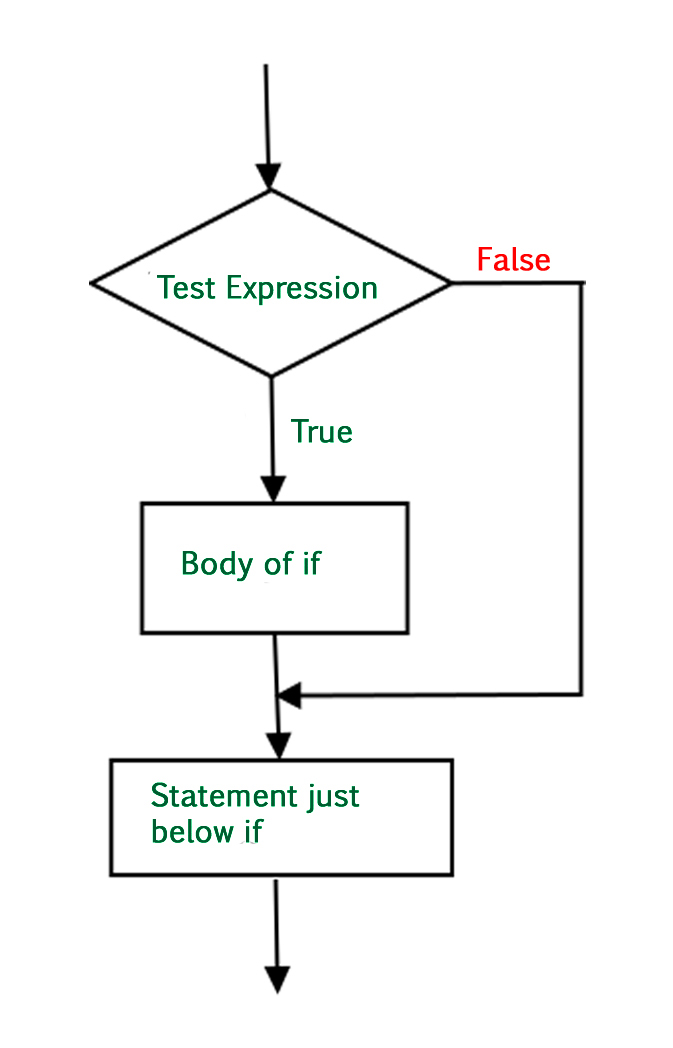
Python if语句流程图
Python if 语句示例
由于 if 语句中存在的条件为假。因此,执行 if 语句下面的块。
- Python3
# python program to illustrate If statement
i = 10
if (i > 15):
print("10 is less than 15")
print("I am Not in if")输出:
I am Not in ifif-else 语句
单独的 if 语句告诉我们,如果条件为真,它将执行一个语句块,如果条件为假,则不会。但是如果我们想在条件为假的情况下做一些别的事情,我们可以使用else语句和if语句一起在if条件为假的时候执行一段代码。
语法:
if (condition):
# Executes this block if
# condition is true
else:
# Executes this block if
# condition is falsePython if-else语句流程图
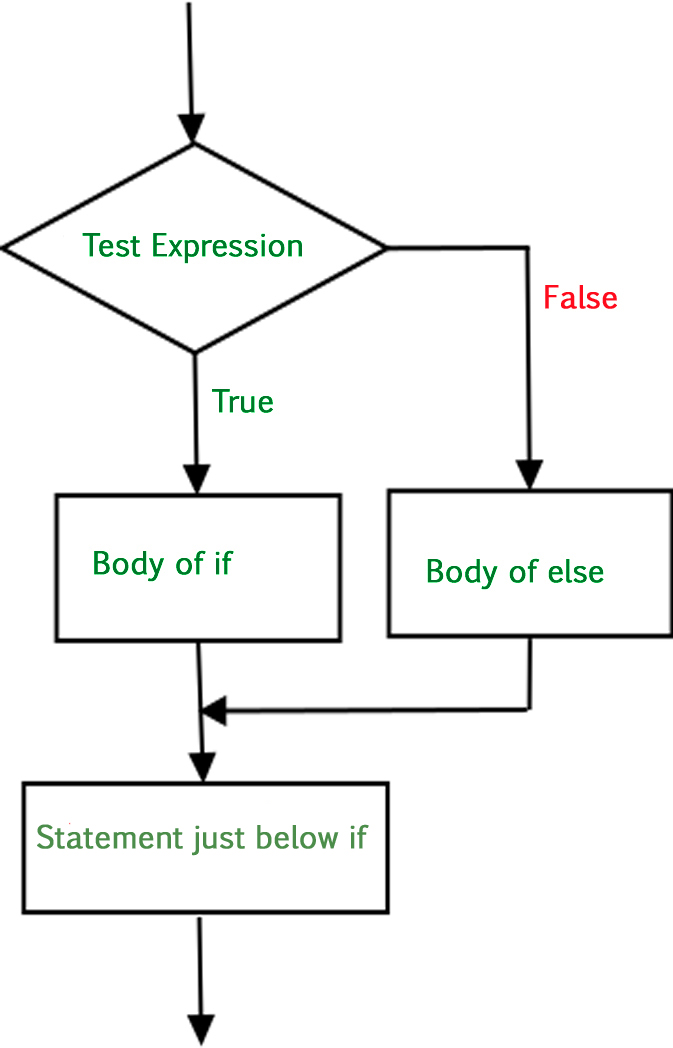
Python is-else语句流程图
Python if-else 语句示例
else 语句后面的代码块在调用不在块中的语句(无空格)后,如果 if 语句中存在的条件为假,则执行该代码块。
- Python3
# python program to illustrate If else statement
#!/usr/bin/python
i = 20
if (i < 15):
print("i is smaller than 15")
print("i'm in if Block")
else:
print("i is greater than 15")
print("i'm in else Block")
print("i'm not in if and not in else Block")输出:
i is greater than 15
i'm in else Block
i'm not in if and not in else Block列表理解中的 Python if else 语句示例
- Python3
# Explicit function
def digitSum(n):
dsum = 0
for ele in str(n):
dsum += int(ele)
return dsum
# Initializing list
List = [367, 111, 562, 945, 6726, 873]
# Using the function on odd elements of the list
newList = [digitSum(i) for i in List if i & 1]
# Displaying new list
print(newList)输出
[16, 3, 18, 18]嵌套 if 语句
嵌套的 if 是一个 if 语句,它是另一个 if 语句的目标。嵌套的 if 语句意味着另一个 if 语句中的 if 语句。是的,Python 允许我们在 if 语句中嵌套 if 语句。即,我们可以将一个 if 语句放在另一个 if 语句中。
语法:
if (condition1):
# Executes when condition1 is true
if (condition2):
# Executes when condition2 is true
# if Block is end here
# if Block is end herePython嵌套if语句流程图
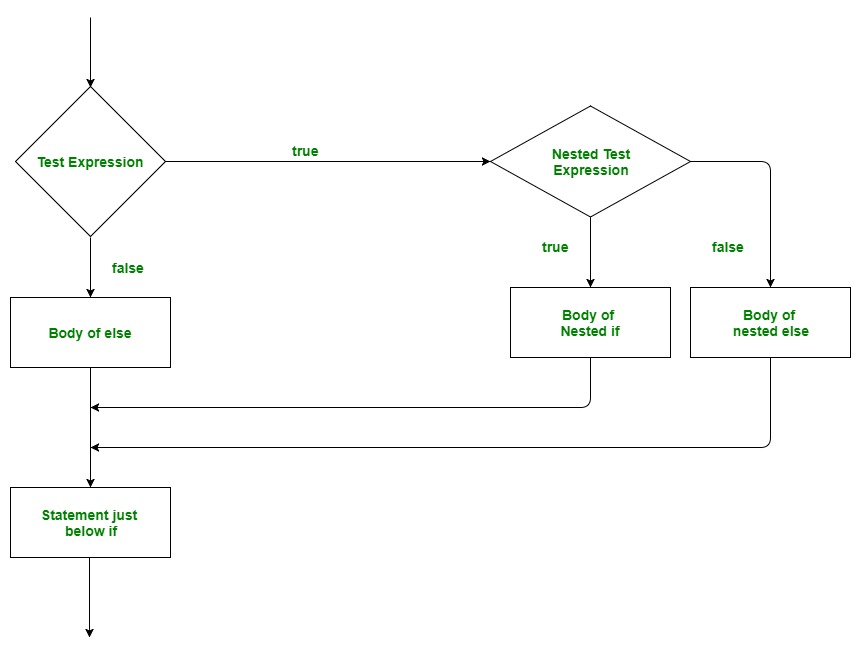
Python嵌套if语句流程图
Python 嵌套 if 语句示例
- Python3
# python program to illustrate nested If statement
#!/usr/bin/python
i = 10
if (i == 10):
# First if statement
if (i < 15):
print("i is smaller than 15")
# Nested - if statement
# Will only be executed if statement above
# it is true
if (i < 12):
print("i is smaller than 12 too")
else:
print("i is greater than 15")输出:
i is smaller than 15
i is smaller than 12 tooif-elif-else 阶梯
在这里,用户可以在多个选项中做出决定。if 语句从上到下执行。一旦控制 if 的条件之一为真,与该 if 关联的语句就会被执行,而梯形图的其余部分将被绕过。如果所有条件都不为真,则执行最后的 else 语句。
语法:
if (condition):
statement
elif (condition):
statement
.
.
else:
statementPython if-elif-else阶梯流程图
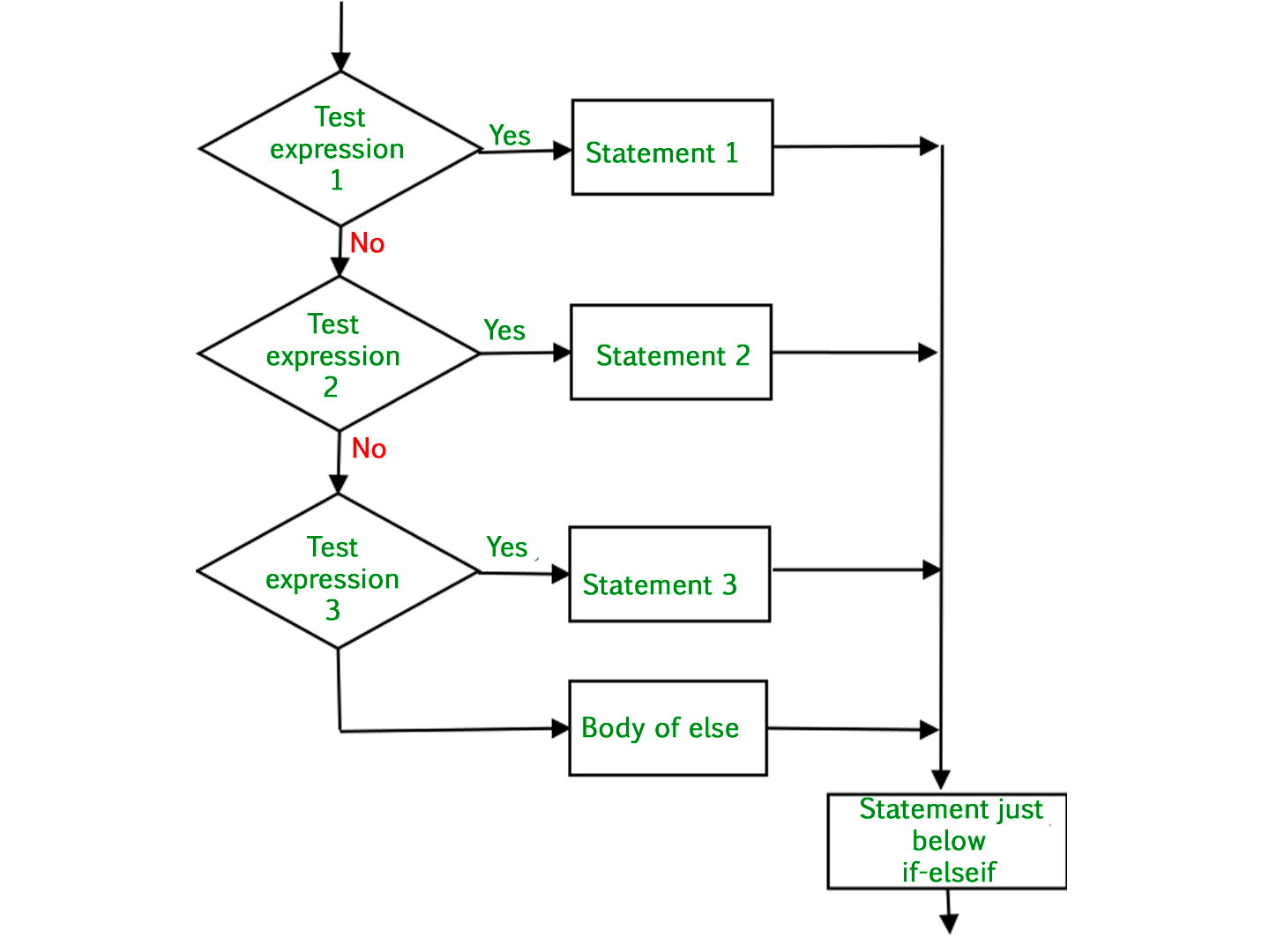
if-elif-else阶梯流程图
Python if-elif-else 阶梯示例
- Python3
# Python program to illustrate if-elif-else ladder
#!/usr/bin/python
i = 20
if (i == 10):
print("i is 10")
elif (i == 15):
print("i is 15")
elif (i == 20):
print("i is 20")
else:
print("i is not present")输出:
i is 20简写 if 语句
每当 if 块中只有一条语句要执行时,可以使用简写 if 。该语句可以与 if 语句放在同一行。
句法:
if condition: statementPython if 简写示例
- Python3
# Python program to illustrate short hand if
i = 10
if i < 15: print("i is less than 15")输出:
i is less than 15简写 if-else 语句
这可用于在单行中编写 if-else 语句,其中 if 和 else 块中只需要一个语句。
句法:
statement_when_True if condition else statement_when_FalsePython if else 简写示例
- Python3
# Python program to illustrate short hand if-else
i = 10
print(True) if i < 15 else print(False)输出:
True原文链接:codingdict.net
