Python 中断语句
Python的break用于终止循环的执行。
Python 中断语句语法:
Loop{
Condition:
break
}Python 中断语句
Python中的break语句用于在触发某些外部条件时将控制带出循环。break 语句放在循环体内(通常在 if 条件之后)。它终止当前循环,即它出现的循环,并在该循环结束后立即恢复执行下一个语句。如果break语句位于嵌套循环内,则break将终止最内层循环。
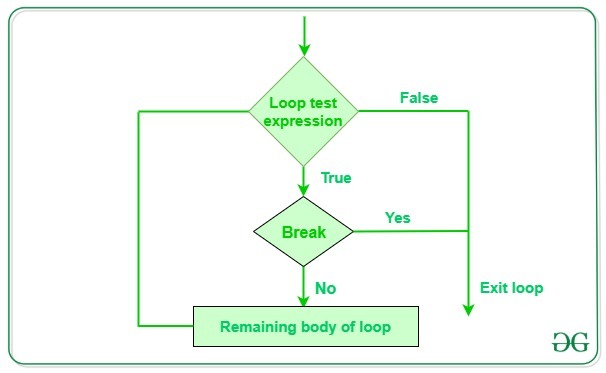
Python 中断语句示例
示例1:
- Python3
for i in range(10):
print(i)
if i == 2:
break输出:
0
1
2示例2:
- Python3
# Python program to
# demonstrate break statement
s = 'geeksforgeeks'
# Using for loop
for letter in s:
print(letter)
# break the loop as soon it sees 'e'
# or 's'
if letter == 'e' or letter == 's':
break
print("Out of for loop" )
print()
i = 0
# Using while loop
while True:
print(s[i])
# break the loop as soon it sees 'e'
# or 's'
if s[i] == 'e' or s[i] == 's':
break
i += 1
print("Out of while loop ")输出:
g
e
Out of for loop
g
e
Out of while loop在上面的示例中,两个循环都在迭代字符串“geeksforgeeks”,并且一旦遇到字符“e”或“s”,如果条件为真,则执行流程将退出循环。
示例3:
- Python3
num = 0
for i in range(10):
num += 1
if num == 8:
break
print("The num has value:", num)
print("Out of loop")输出
The num has value: 1
The num has value: 2
The num has value: 3
The num has value: 4
The num has value: 5
The num has value: 6
The num has value: 7
Out of loop在上面的例子中,迭代到num=7后,num的值为8,并且遇到了break,因此执行流程被带出循环。
在 Python 中使用循环可以高效地自动执行和重复任务。但有时,可能会出现这样的情况:您希望完全退出循环、跳过迭代或忽略循环的某些语句,然后再继续循环。这些可以通过称为跳转语句的循环控制语句来完成。循环控制或跳转语句改变其正常顺序的执行。当执行离开作用域时,在该作用域中创建的所有自动对象都将被销毁。Python 支持以下控制/跳转语句。
原文链接:codingdict.net
